FTT Token

What Is the FTT Token?
The FTT token is the platform token introduced by the FTX ecosystem, designed to provide utility within its business framework. Its key functions include trading fee discounts, margin collateral, and staking benefits. Platform tokens are issued by specific exchanges, granting holders unique use cases and privileges tied directly to the platform’s operations and overall health.
FTT was originally designed with a buyback and burn mechanism, where a portion of platform revenue was used to periodically purchase and burn FTT, thus reducing supply. Token burning refers to sending tokens to an inaccessible address, removing them from circulation permanently. Staking involves locking tokens in a contract or on the platform in exchange for rights or rewards. These mechanisms are dependent on the platform’s ongoing operations—at present, users should refer to official announcements for current status.
Current Price, Market Cap, and Circulating Supply of FTT (FTT)
As of 2026-01-22 (data source: provided input), FTT is priced at approximately $0.4961, with a circulating supply of about 328,895,103.81 tokens.
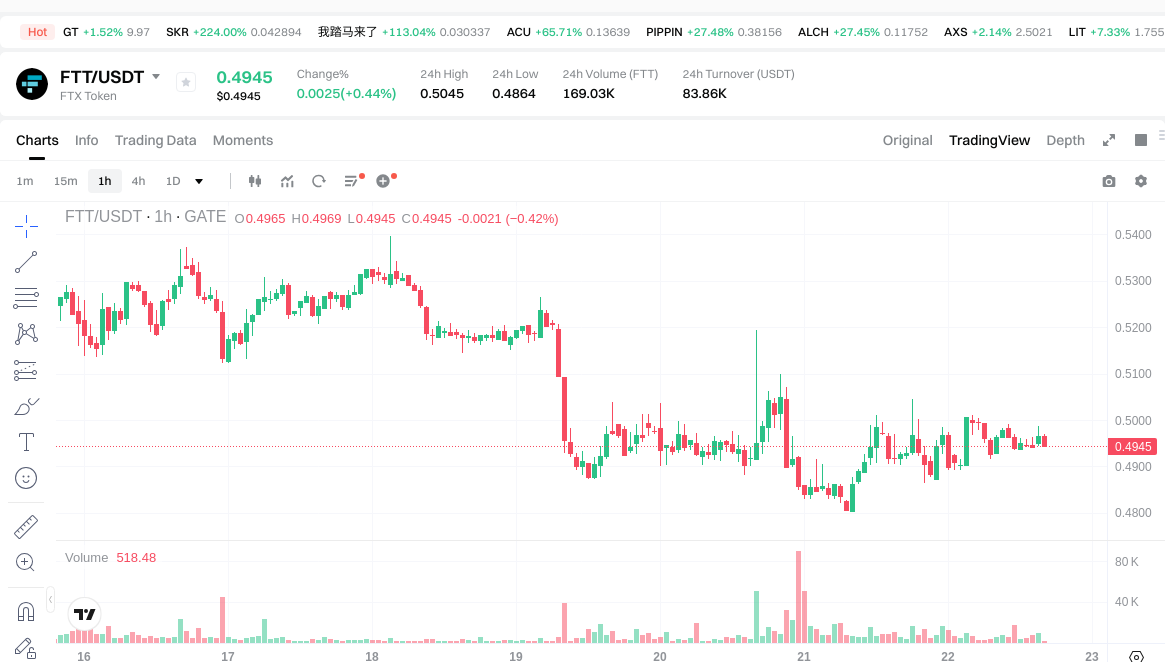
View FTT USDT Price
The circulating market cap is roughly $163.16 million, with a fully diluted market cap also at about $163.16 million, representing approximately 0.005% of the total crypto market. In the past hour, the price changed by -0.38%; over 24 hours, +0.97%; in 7 days, -5.77%; over 30 days, +1.70%; with a 24-hour trading volume of around $85,200.
Market cap is calculated as “price × circulating supply” and serves as an indicator of a token’s overall market size. Fully diluted market cap is “price × maximum supply”, reflecting the potential valuation if all tokens are released. Currently labeled as “Inactive”, indicating low project activity or limited trading pairs, which may result in increased liquidity and price volatility risks.
Who Created the FTT Token (FTT) and When?
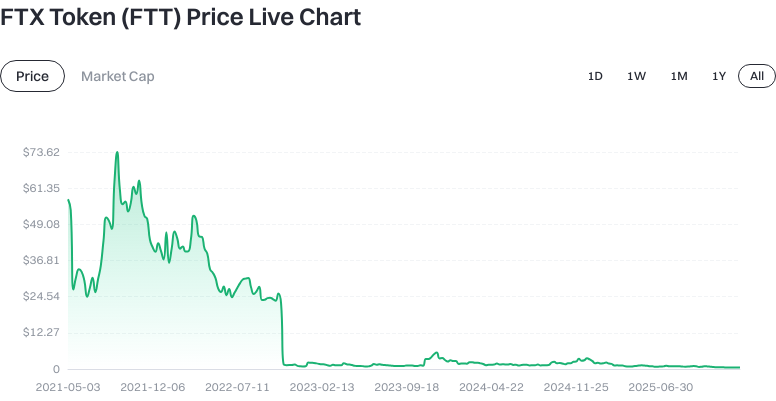
FTT was launched on July 28, 2019 by the FTX ecosystem team as a utility token to support functions such as fee discounts, collateralization, and staking rights within its business suite. In November 2022, entities associated with FTX entered bankruptcy protection and subsequent restructuring processes (sources: public court filings and company announcements as of October 2024). As a result, FTT’s functionality and value anchors have become uncertain, and holders should closely monitor restructuring updates and official disclosures.
How Does the FTT Token (FTT) Work?
FTT’s operation centers on its “use cases + tokenomics.” Use cases include trading fee discounts, margin collateral for contracts, and staking for voting or rewards. The tokenomics involve buybacks and burns: a fixed proportion of platform revenue was used to buy back FTT regularly and burn it, creating a logical expectation of “supply contraction.”
Margin collateral refers to using held assets as risk protection in derivatives trading. Staking means locking tokens to earn rights or rewards. All these mechanisms depend on platform operations and enforcement of rules. At present, actual execution of buybacks, burns, and staking benefits should be verified against official updates—do not rely solely on historical information.
What Can You Do With the FTT Token (FTT)?
Historically, holders could access trading fee discounts, use FTT as margin collateral, participate in voting and airdrops on the platform. For everyday users, these features resemble a combination of “membership levels + collateralized credit,” helping reduce costs and enhance user experience.
Given current circumstances, if related services are unavailable, these use cases may not be functional. At this stage, FTT primarily acts as a transferable crypto asset for on-chain transfers and secondary market trading. Restoration of original utilities depends on platform restructuring and regulatory developments.
What Are the Main Risks and Regulatory Issues With FTT Token (FTT)?
Primary risks are linked to the platform itself—FTT’s value is tightly bound to the business health of its issuing platform. If the platform faces operational or restructuring uncertainty, demand for the token and its buyback mechanism may fail to materialize.
Liquidity and price risk are also significant. The “Inactive” label suggests shallow trading depth and heightened volatility, especially during news-driven events.
Legal and regulatory risks must be considered. Different jurisdictions may apply various rules to platform tokens; some regions may classify them as securities or require specific disclosures. Users should understand local laws and tax requirements.
Finally, custody and operational risk are critical. Whether held on an exchange or in self-custody wallets, protection against private key leaks and account theft is essential. Private keys are fundamental for accessing crypto assets; their loss or exposure results in irreversible losses.
What Is the Long-Term Value Proposition of FTT Token (FTT)?
Potential long-term value hinges on three factors: first, the pathway and pace of platform restructuring and business recovery, which will determine if original use cases return; second, whether tokenomics like buybacks, burns, and fixed supply can be sustained; third, if trust can be rebuilt around the brand and community to drive genuine usage demand.
Challenges include high dependency on the platform, regulatory uncertainty, and possible prolonged interruption of utility functions. For long-term observers, pragmatic tracking of legal developments, operational updates, and on-chain data is advised—base decisions on evidence rather than pure speculation.
How Can I Buy and Safely Store FTT Token (FTT) on Gate?
If Gate has listed FTT, follow these steps; if you cannot find trading pairs in search results, direct purchase is currently unavailable on Gate—add it to your watchlist and monitor listing announcements; avoid buying through unofficial channels.
Step 1: Register and complete KYC verification using your personal ID—this improves account security and withdrawal limits.
Step 2: Prepare funds by depositing fiat or stablecoins like USDT; confirm deposit networks and fees.
Step 3: Search for “FTT” in the trading interface; verify token identifiers and contract details; check for spot trading pairs and risk warnings.
Step 4: Place your order—limit orders offer more control based on liquidity; set reasonable price/quantity parameters; after execution, check your holdings on the asset page.
Step 5: Withdraw and store securely—if self-custody is preferred, start with a small test transaction; then withdraw to your wallet address using the same network. Enable withdrawal whitelist, two-factor authentication (2FA), and anti-phishing codes to lower account risks.
For storage options: Hot wallets are connected to the internet—convenient for trading but higher risk of cyber attacks; cold wallets are offline/hardware devices storing private keys—more secure but less convenient. Backup mnemonic phrases offline and distribute them securely; never upload photos or store them with your device.
How Is FTT Token (FTT) Different From Ethereum?
Positioning: FTT is a platform token whose value depends on its issuing exchange; Ethereum (ETH) is a native asset of a public blockchain used to pay gas fees and secure network operations.
Use cases: FTT focuses on fee discounts, collateralization, and platform-specific rights; ETH powers smart contracts, DeFi, NFTs, and broad ecosystem activities.
Supply & mechanism: FTT supply is fixed with a past buyback/burn model; ETH introduced base fee burning with EIP-1559—net issuance is now affected by on-chain activity.
Risk profile: FTT faces platform dependency and regulatory uncertainty; ETH relies more on network security and robust decentralized consensus.
Summary of FTT Token (FTT)
FTT is essentially a utility token tightly linked to platform operations—it previously formed a value loop via fee discounts, collateralization, staking rights, buybacks, and burns. Current data indicates a small market cap with low activity; utility availability and demand are uncertain. For typical investors, it’s crucial to monitor restructuring progress, compliance updates, trading pair accessibility, and liquidity changes—and check Gate listings for market depth before engaging. Best practice includes testing small transfers first, enabling security settings, using self-custody where possible, and avoiding unofficial purchase channels. Only when real-world utilities return with regulatory support can FTT’s value logic be properly validated.
FAQ
Does FTT Token Have Value After FTX’s Collapse?
FTT’s value is closely tied to FTX’s operational status. After the collapse of FTX, FTT’s price dropped sharply but remains tradable as a blockchain asset on secondary markets. Investors should carefully assess risks—the future value depends on whether another ecosystem can sustain its use cases.
What Real Benefits Can I Get From Holding FTT Tokens?
During FTX’s operation period, holders enjoyed trading fee discounts and revenue sharing benefits. Since the collapse of FTX, these benefits have largely ceased to exist. Currently FTT mainly exists as a tradable asset—potential gains come only from market price movements.
How Should Beginners Understand Risks With FTT Token?
The greatest risk with FTT is its strong dependence on its originating platform—most value derives from FTX itself. Platform incidents directly affect token value (as seen with the FTX case). Be wary of liquidity risks and market volatility; ensure you fully understand these factors before investing.
How Is FTT Token Different From Other Exchange Tokens Like BNB?
Exchange tokens’ value generally tracks the health of their issuing exchange. BNB continues to create value through Binance’s robust ecosystem growth; FTT lost its core use cases after FTX collapsed. When choosing exchange tokens, focus on evaluating exchange stability and actual utility prospects for each token.
Where Can I Safely Trade and Store FTT Tokens?
FTT can be traded on major platforms like Gate. For storage, hardware wallets (such as Ledger) or secure custody solutions are recommended—avoid leaving assets on exchanges long-term. Always verify platform security certifications; use strong passwords and enable two-factor authentication for account protection.
Quick Reference Glossary for FTT (FTT)
- Exchange Token: A token issued by cryptocurrency exchanges used for paying trading fees, participating in governance, or accessing platform-specific benefits.
- Fee Discount: Holding exchange tokens may qualify users for reduced fees during trading or withdrawals.
- Liquidity Mining: Mechanism where users provide liquidity to trading pairs or participate in platform activities to earn token rewards.
- Governance Voting: Token holders may participate in major exchange decisions or feature upgrades.
- Burn Mechanism: Periodic destruction of a portion of tokens by the platform to decrease supply and increase value for remaining holders.
- Staking Yield: Users locking up tokens can earn interest or share in platform revenue distribution.
References & Further Reading About FTT Token (FTT)
-
Official Website / Whitepaper:
-
Development / Documentation:
-
Authoritative Media / Research:
Related Articles

In-depth Explanation of Yala: Building a Modular DeFi Yield Aggregator with $YU Stablecoin as a Medium

Sui: How are users leveraging its speed, security, & scalability?
